Introduction: Understanding Diabetes
Imagine waking up one day, only to realize that your health is slipping out of control, quietly influenced by choices you didn’t know were significant. Diabetes is a chronic condition affecting millions worldwide, and while it may seem mysterious, its causes are largely rooted in factors we can understand and influence.
This blog delves deep into the main causes of diabetes, offering clarity, actionable insights, and hope. Whether you’re seeking to prevent the condition or understand it better, this guide is your starting point.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder where the body struggles to regulate blood sugar (glucose) levels. Glucose is essential for energy, but too much or too little can lead to severe health complications.
There are primarily three types of diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing cells.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The most common type, linked to lifestyle factors and insulin resistance.
- Gestational Diabetes: Occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after delivery.
Each type has unique triggers, but some causes overlap. Let’s explore these in detail.
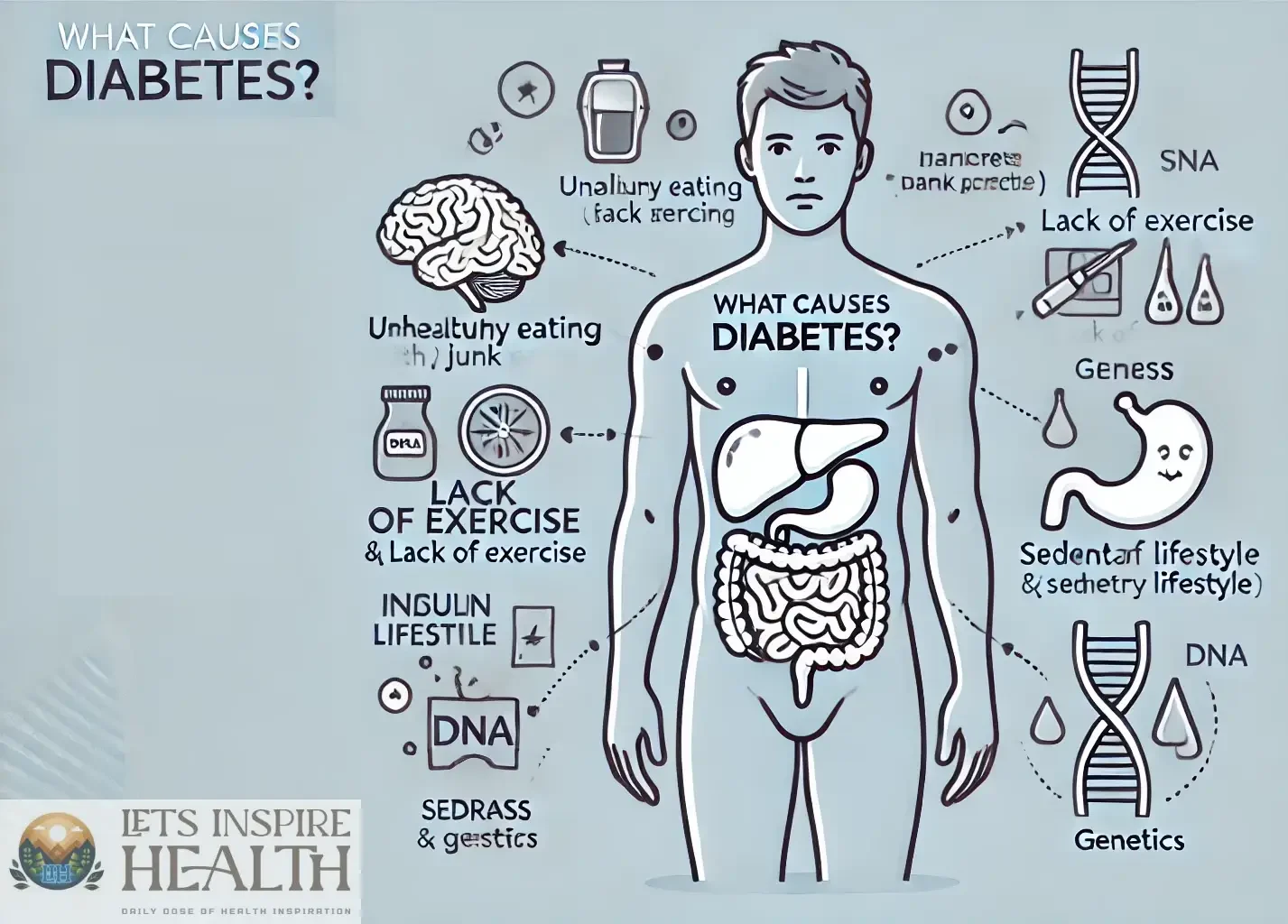
Main Causes of Diabetes
1. Genetics: Is It in Your DNA?
Some people inherit a higher risk of developing diabetes. If you have a family history of the condition, your chances increase.
Real-World Example
Think of Anna, whose mother and grandmother both had Type 2 diabetes. Despite her healthy lifestyle, Anna was diagnosed at 45. Genetic testing revealed she had markers for insulin resistance, highlighting the hereditary aspect.
Can You Prevent It?
While genetics can’t be altered, lifestyle changes like a balanced diet and regular exercise can delay or even prevent onset.
2. Lifestyle Choices: The Silent Triggers
a. Unhealthy Diet
Diet plays a pivotal role in diabetes. Diets rich in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can lead to obesity, a significant risk factor.
Checklist for a Healthy Diet:
- Include whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Limit sugar-sweetened beverages.
- Focus on lean proteins like chicken and fish.
b. Lack of Physical Activity
A sedentary lifestyle increases insulin resistance. Exercise helps your body use glucose more effectively.
Step-by-Step Tutorial:
- Start with 30 minutes of brisk walking daily.
- Gradually add strength training twice a week.
- Track progress with a fitness app.
3. Obesity: The Gateway to Diabetes
Obesity, especially abdominal fat, disrupts how insulin works in the body. According to studies, over 85% of Type 2 diabetes cases are linked to being overweight.
Comparison Table: Healthy Weight vs. Overweight Risk
| Factor | Healthy Weight | Overweight |
| Insulin Sensitivity | Normal | Reduced |
| Blood Sugar Control | Stable | Unstable |
| Risk of Diabetes | Low | High |
4. Stress and Hormonal Changes
Chronic stress increases cortisol, a hormone that raises blood sugar levels. Stressful jobs, family conflicts, and financial struggles can all contribute.
Stress Management Tips:
- Practice mindfulness or yoga.
- Maintain a regular sleep schedule.
- Seek professional counseling when needed.
5. Medical Conditions and Medications
Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and medications such as steroids can increase diabetes risk. Regular check-ups are essential if you’re managing such conditions.
6. Environmental Factors: Beyond Your Control
Exposure to toxins or viral infections may trigger autoimmune responses, especially in Type 1 diabetes.
Real-World Example
A study revealed that children exposed to certain viruses were more likely to develop Type 1 diabetes. While this is rare, it highlights the complexity of diabetes triggers.
How to Prevent Diabetes: Actionable Tips
- Maintain a Healthy Diet
Follow a Mediterranean or plant-based diet. - Stay Active
Aim for 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly. - Monitor Your Health
Regular blood sugar checks can catch prediabetes early. - Manage Stress
Incorporate stress-relief practices into your routine. - Get Regular Check-Ups
Discuss your family history and risk factors with your doctor.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Health
While the causes of diabetes are multifaceted, understanding them empowers you to make informed decisions. Genetics may set the stage, but your lifestyle choices determine much of the outcome.
By adopting healthier habits today, you can significantly lower your risk and lead a fulfilling life. Diabetes is not just a diagnosis; it’s a wake-up call for better health.