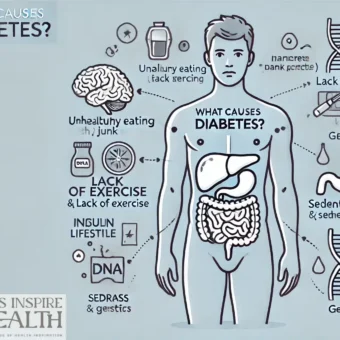
Imagine a world where you’re not constantly checking your blood sugar, meticulously tracking your carb intake, and worrying about the potential long-term effects of diabetes. While managing diabetes requires ongoing effort, recent technological advancements are dramatically changing the game. This isn’t about replacing traditional care; it’s about empowering you with smarter tools to proactively manage your health. Let’s explore how tech can revolutionize your diabetes journey, offering insights, streamlining processes, and ultimately, helping you live a fuller, healthier life.
Smart Blood Glucose Monitoring Systems
Traditional blood glucose meters, while effective, can be cumbersome and require manual data entry. Smart blood glucose monitoring systems have emerged to address these challenges. These systems seamlessly integrate with smartphones and cloud platforms, offering a more convenient and comprehensive view of your glucose levels.
How they work: These systems utilize continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) – small sensors inserted under the skin that constantly measure glucose levels. The data is transmitted wirelessly to a receiver or smartphone app, providing real-time insights. Many CGMs also integrate with insulin pumps, allowing for automated insulin delivery based on glucose readings.
Pros:
- Real-time data: Immediate access to glucose levels, allowing for rapid adjustments to diet and activity.
- Trend analysis: CGMs track glucose trends over time, revealing patterns and helping you understand how different factors – food, exercise, stress – impact your levels.
- Reduced finger pricks: While not completely eliminating finger pricks (calibration checks are still needed), CGMs significantly reduce the frequency.
- Remote monitoring: Enables healthcare providers to remotely monitor your glucose levels and provide timely support.
Cons:
- Cost: CGMs and related accessories can be expensive, although insurance coverage is improving.
- Calibration: Regular calibration with finger pricks is still required.
- Sensor discomfort: Some users experience skin irritation or discomfort from the sensor.
Effects on Human Health: The immediate feedback provided by CGMs allows for proactive adjustments, minimizing the risk of both hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), leading to improved overall health outcomes and reduced complications.
Connected Insulin Pumps
Connected insulin pumps represent another significant advancement. These pumps are equipped with Bluetooth connectivity, enabling them to communicate with smartphones and other devices. This connectivity unlocks a host of new capabilities.
How they work: These pumps deliver precise doses of insulin based on pre-programmed settings or, in advanced models, real-time glucose data from CGMs. The smartphone app allows users to remotely adjust settings, track insulin delivery, and receive alerts.
Pros:
- Automated insulin delivery: Reduces the burden of manual insulin injections.
- Personalized insulin delivery: Algorithms can be tailored to individual needs and lifestyles.
- Reduced cognitive load: Simplifies the process of managing insulin.
- Improved glycemic control: Leads to tighter control of blood glucose levels.
Cons:
- Complexity: Requires careful programming and ongoing monitoring.
- Dependence on technology: Malfunctions can disrupt insulin delivery.
- Cost: Connected insulin pumps are generally more expensive than traditional pumps.
Effects on Human Health: The precision of connected insulin pumps, coupled with real-time glucose data, dramatically improves glycemic control, minimizing the risk of long-term complications such as nerve damage, kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease.
Smart Food Trackers and Apps
Managing diabetes effectively hinges on understanding the impact of food on blood glucose levels. Smart food trackers and apps are streamlining this process, making it easier than ever to monitor carbohydrate intake and make informed food choices.
How they work: These apps allow users to scan barcodes of food products, automatically retrieve nutritional information, and track carbohydrate counts. Many apps also provide recipe suggestions and meal planning tools.
Pros:
- Simplified carbohydrate tracking: Eliminates the need for manual calculations.
- Personalized meal planning: Helps users create meals that align with their individual needs.
- Increased awareness: Promotes a greater understanding of food’s impact on blood glucose.
Cons:
- Accuracy of data: Relies on the accuracy of nutritional information provided by the app.
- User effort: Requires diligent tracking of food intake.
Effects on Human Health: Precise carbohydrate tracking, facilitated by smart food trackers, empowers users to make informed food choices, contributing to better glycemic control and reducing the risk of complications.
Digital Health Platforms and Remote Monitoring
The rise of digital health platforms is transforming diabetes care. These platforms integrate data from various sources – CGMs, insulin pumps, food trackers, activity trackers – to provide a holistic view of the patient’s health. They also facilitate remote monitoring by healthcare providers.
How they work: These platforms utilize cloud-based technology to securely store and analyze patient data. Healthcare providers can access this data remotely, allowing for timely interventions and personalized support.
Pros:
- Comprehensive data analysis: Provides a holistic view of the patient’s health.
- Remote monitoring: Enables healthcare providers to monitor patients remotely.
- Personalized care: Supports tailored treatment plans.
Cons:
- Data security and privacy: Concerns about data security and privacy.
- Connectivity issues: Requires reliable internet connectivity.
Effects on Human Health: The integration of data and remote monitoring enhances care coordination, leading to improved glycemic control, reduced hospitalizations, and better overall health outcomes.
Summary
The technological advancements discussed – smart blood glucose monitoring systems, connected insulin pumps, smart food trackers, and digital health platforms – are revolutionizing diabetes management. By providing real-time data, automating processes, and facilitating remote monitoring, these tools empower individuals to take control of their health and dramatically improve their outcomes. While challenges remain, such as cost and data security, the potential benefits of leveraging technology in diabetes care are undeniable. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative solutions to emerge, further transforming the lives of people living with diabetes.
**Disclaimer:** *This blog post is intended for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. It is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment. The information provided here should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.*