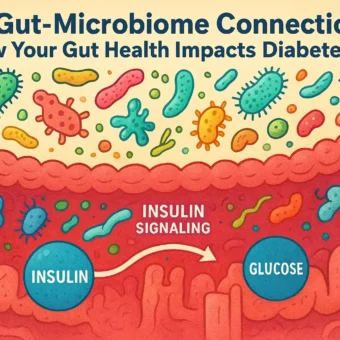
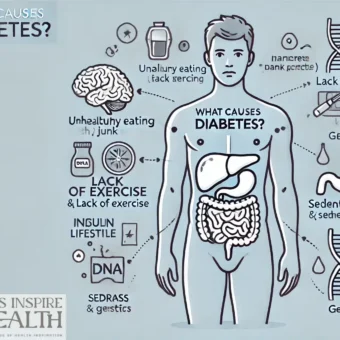
Diabetes is sometimes referred to be a silent killer because it is a chronic disorder that impacts how your body converts food into energy. This is due to the fact that it may develop gradually and present with modest symptoms that are simple to ignore. However, for prompt diagnosis and treatment, it is essential to identify the early warning signs of diabetes.
We’ll examine the five most typical indicators of diabetes in this blog post. You can take proactive measures to maintain your health and avoid major consequences by being aware of these warning signs.
1. Frequent Urination
One of the most common early signs of diabetes is frequent urination, especially at night. This condition, known as polyuria, occurs when your kidneys produce excess urine due to high blood sugar levels. Your body tries to flush out the excess sugar by increasing urine production.
2. Excessive Thirst
Increased thirst, or polydipsia, often accompanies frequent urination. As your body loses fluids through frequent urination, you may feel constantly thirsty, even after drinking plenty of water.
3. Unexplained Weight Loss
Sudden, unexplained weight loss can be a significant warning sign of diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes. When your body can’t use glucose effectively, it turns to burning fat and muscle for energy, leading to weight loss.
4. Blurred Vision
High blood sugar levels can affect the lens of your eye, causing it to swell and change shape. This can lead to blurry vision, which may improve as your blood sugar levels stabilize.
5. Fatigue and Weakness
Feeling constantly tired and weak, even after getting enough sleep, can be a sign of diabetes. When your body can’t use glucose for energy, it can lead to fatigue and a lack of energy.
Risk Factors for Diabetes
While anyone can develop diabetes, certain factors increase your risk:
- Family History: If you have a family member with diabetes, your risk is higher.
- Age: The risk of type 2 diabetes increases with age.
- Obesity: Excess weight, especially around the waist, can contribute to insulin resistance and diabetes.
- Physical Inactivity: Lack of physical activity can increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- High Blood Pressure: High blood pressure is often associated with insulin resistance and diabetes.
- High Cholesterol: High cholesterol levels can increase your risk of heart disease and diabetes.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans, Hispanic Americans, American Indians, and Asian Americans, have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Preventing Diabetes
While you can’t always control your risk factors, you can take steps to prevent or delay the onset of diabetes:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Aim for a healthy weight and waist circumference.
- Eat a Healthy Diet: Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
- Regular Physical Activity: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Limit Sugar and Processed Foods: Reduce your intake of sugary drinks and processed foods.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-management techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing.
- Regular Check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your blood sugar levels and other risk factors.
If you experience any of the warning signs of diabetes, it’s essential to consult your healthcare provider for a diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. Early detection and management of diabetes can help prevent serious complications and improve your overall health.